
Three-quarters of hospitals and health systems increased their IT spending last year, and many will continue to focus on strengthening their IT infrastructure and cybersecurity, according to a new report from Bain & Company and KLAS Research. He says he will continue to do so.
The findings are based on a survey of 150 provider organizations and payers across the United States.
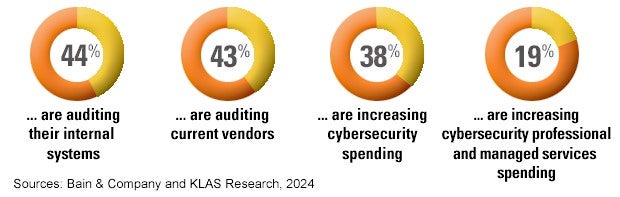
The greater attention many providers are paying to strengthening their cybersecurity defenses is a direct response to the hack of payments management company Change Healthcare in February, the report said. This cyberattack was one of the largest in U.S. history and had a significant impact on U.S. hospitals and healthcare systems. 94% of AHA members reported being financially impacted by this event, and more than half said the impact was “significant or severe.”
The incident also prompted many hospital boards to consider single points of vulnerability within their IT stacks, leading organizations to allocate funds to increase redundancy in critical systems, the report said. states.
This study found the following regarding provider responses to the Change Healthcare attack:
For more information on how to prevent and respond to cyber threats, visit the AHA Cybersecurity and Risk Advisory webpage.
Other categories of technology investments that stood out in the survey data include improvement efforts such as:
Optimize clinical workflow. Data platforms and interoperability. Revenue cycle management.
Providers responding to the survey said they want to streamline processes, reduce administrative burden, and increase utilization of labor, capital equipment, and equipment. Data and analytics platforms are also under scrutiny, with many organizations realizing that data quality and governance are not robust enough to optimize the value of data-driven decision-making.
“With the prospect of more powerful solutions enabled by artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, data quality supports clinical decision-making and non-clinical use cases such as patient assistance and data loss prevention. “This is accelerating the pace of improvement,” the report states.
Cost control, electronic health record integration, and system interoperability continue to challenge provider IT. Providers cited cost as their biggest challenge in 2023, highlighting a persistent problem.
Expected to expand adoption of AI
Healthcare providers are seeking AI-supported solutions to enhance decision-making, improve operational efficiency, and deliver care. However, only 15% say they have an AI strategy in place, compared to 5% in 2023. For comparison, approximately 25% of payers say they currently have an established AI strategy.
However, both types of organizations say they are optimistic about the adoption of generative AI.
The report states that providers are beginning to pilot generative AI in clinical applications such as documentation and decision support tools. Early trials look promising, suggesting that AI-powered tools may one day be able to analyze large amounts of data, identify patterns and trends, and generate actionable insights. Masu. Pilots around ambient clinical documentation have been particularly successful in reducing administrative burden for clinicians and improving the patient experience.

