Research design, setting, population
A retrospective observational study of the entire HCWS population at university hospitals (6000 HCWS) was conducted. All of these were subjected to health surveillance in accordance with Italian laws regarding the protection of workers at occupational risk (D.LGS. 81/2008) and covered three years (January 1st 2020 to December 31st 31st 31st 31st).
Prevention protocols: risk assessment, variables of interest, data collection
The Preventive Surveillance Protocol was established by the operative unit of occupying medicine for all HCWs working at Bari University Hospital in Apria, southern Italy. Upon request for protocols, all HCWs were subjected to measurements of systolic blood pressure (SBP) (SBP), secondary blood pressure (DBP) (DBP) (DBP) during health monitoring conducted in accordance with Italian law regarding the protection of workers at occupational risk (D.Lgs. 81/2008). BP was measured according to the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association guidelines 17 for the prevention, detection, assessment and management of high BP in adults 17. Traditional methods of brachial artery hearing with a stethoscope were used either in a sitting or in a supine position, recording BP with both arms, and using the arm for higher readings for two or more subsequent measurements. To estimate workers' BP, two or more measurements averaged over two or more times were used.
Family, physiology, occupation, and pathological history were recorded in each HCW health record as part of a health monitoring visit. Additionally, at the same time, all workers underwent electrocardiogram (ECG) and blood sampling, followed by total cholesterol (C-TOT; MG/DL), high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C; MG/DL), low density lipotan cholester (LDL-C; Thl-C/DL), and This (LDL-C; DL). Mg/dl), blood glucose (GLC; Mg/DL), red blood cell sedimentation rate (ESR; MM/H), C-reactive protein (C-RP; Mg/L), and other routine blood indicators (e.g., indicators of thyroid and renal function) were implemented for healthcare protocols for healthcare providers for empirical workers. Samples were analyzed at the Hospital Analysis Institute using standardized methods, and the usual range of these parameters was defined according to the gender and age of workers and reference values established by international guidelines and literature data.
All workers were categorized into Italian Law on Occupational Risk Assessment (D.LGS 81/08) and other studies conducted on the same cohort of workers. technicians, medical professional students) and non-healthcare workers (including administrative staff, auxiliary staff, cleaners, drivers, lawyers, librarians, pastors, doormen, technical workers, etc.).
The main CVDs were divided into five categories. Rhythm disorder (RD; Tatia arrhythmias, brady arrhythmias, conduction defects). Anatomical dysfunction (AFD; for example, anatomical and/or motor changes in the valve structure, walls and/or cardiac ward, chronic heart failure NYHA I-IV); ischemic disorders (ID; ischemic cardiomyopathy, ischemic stroke, stable angina, unstable angina); hypertension disorders (HD; e.g. grade I, II, III arterial hypertension, isolated contractile hypertension, hypertensive heart disease); other CVDs (OD; endocarditis, myocarditis, pericarditis, other pericardial pathology, large extracardial vascular pathology, peripheral arterial disease).
Based on the findings of the study, a risk assessment was performed to define a high-risk HCW (HR-HCW) as a subject suffering from one or more of the following conditions: pathological history of CVD (e.g., rhythm disorders, anatomical disorders, ischemic disorders, hypertension disorders, other cardiac therapy); changes identified during physical examinations of the cardiovascular system (PE) (e.g., heart murmur, rhythm changes, pericardial friction, blood pressure changes); changes in ECG performed during health monitoring tests (e.g., arrhythmia, changes in PR intervals, QRS, T-waves, conduction defects, ventricular repolarization changes); new onset of cardiac-related covid-19-related symptoms (e.g., dyspnea, chest pain, motion pat, cardiac murmur, pericardial friction). To aim for the highest level of prevention, all deviations from normality, even those commonly interpreted as non-pathological (e.g., incomplete right bundle branch blocks), were considered to be worthy of further investigation with specialized cardiac disease tests and therefore considered “high risk” in relation to prevention protocols.
All remaining HCWs were classified as low risk (LR-HCWS). In the latter case, no further investigation was required, and regular clinical reevaluations were established outside of data collection for this study. On the contrary, all HR-HCWs received specialized cardiac disease tests and final further diagnostic instrumental tests requested by experts (e.g., echocardiography, transcranial Doppler with bu worm tests, exercise stress tests on treadmill or cycle ergometers, 24-hour ECG records, fascia perfusion muscle muscle body, muscle packaging sclerosis, muscle packaging therapy records, hospitalisation). In the case of cardiac disease tests, if negative for CVDS, HR-HCW was subjected to regular reevaluation at a frequency established by health monitoring protocols other than data collection for this study. For new onset and/or already known CVDS diagnosis, HR-HCW was regularly reevaluated at a higher frequency, established by cardiologists.
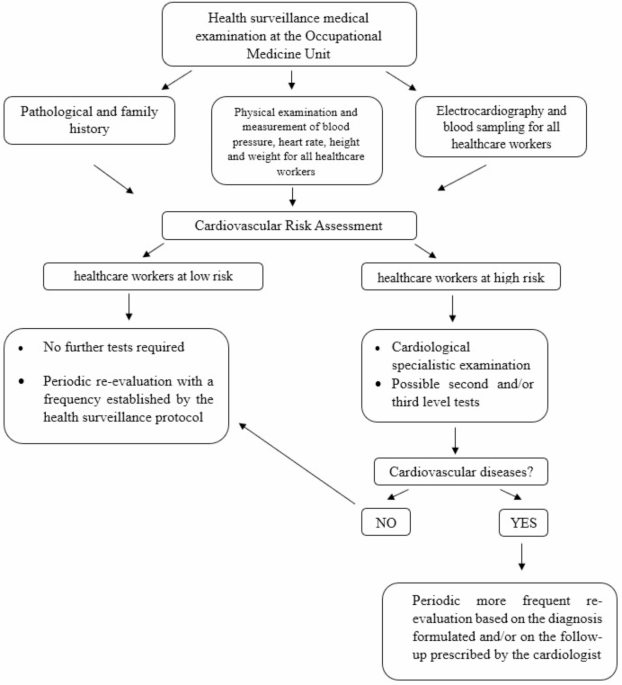
Health monitoring protocols established by the Occupational Medicine Unit are summarized in the diagram below (Figure 1).
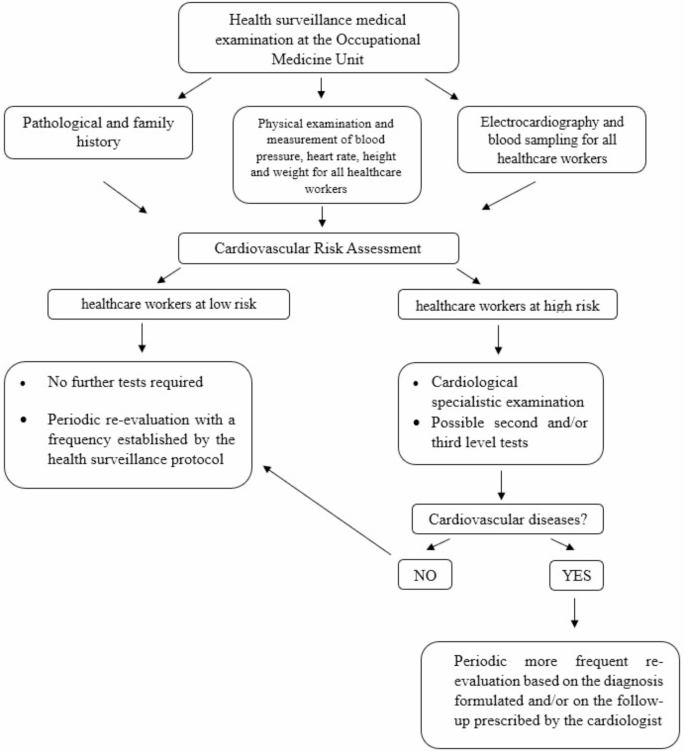
Preventive surveillance protocols to manage cardiovascular risks in healthcare workers.
All HCWs were informed that data will be treated anonymously and collectively for scientific purposes, in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Statistical analysis
The analysis was performed using STATA MP18 software. Continuous variables were expressed as mean ± standard deviation and range. Categorical variables were expressed as ratios. The normality of continuous variables was assessed using skewness and kurtosis tests, but we were unable to construct a normalized model for people who were not normally distributed. Continuous variables were compared across multiple groups using the Kruskall – Wallis nonparametric test. Categorical variables were compared across groups using Chi-square tests or Fisher exact tests. Multivariate logistic regression was used to assess the association between CVD diagnosis and the same determinants and the same determinants. Adjusted odds ratio (AOR) was calculated and 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs) were shown. Pearson's chi-square test was used to assess the fit of the multivariate logistic regression model. In all tests, a p-value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
statement
Patients were informed that data from the research protocols will be treated for scientific purposes based on scientific methods, in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations, and for scientific purposes based on the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Ethical approval was not required as all medical and instrumental testing was carried out in accordance with Italian law regarding the protection of workers at occupational risk (D.Lgs. 81/2008). Nevertheless, this study was approved by Ajienda Oz Ospedaliero Univers Talilia Consoligier Polinico (Parair Studio N. 7241) of Bali.
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.