Why Health Care
Healthcare has always been an attractive target for threat actors, one of the top five industries targeted by ransomware.
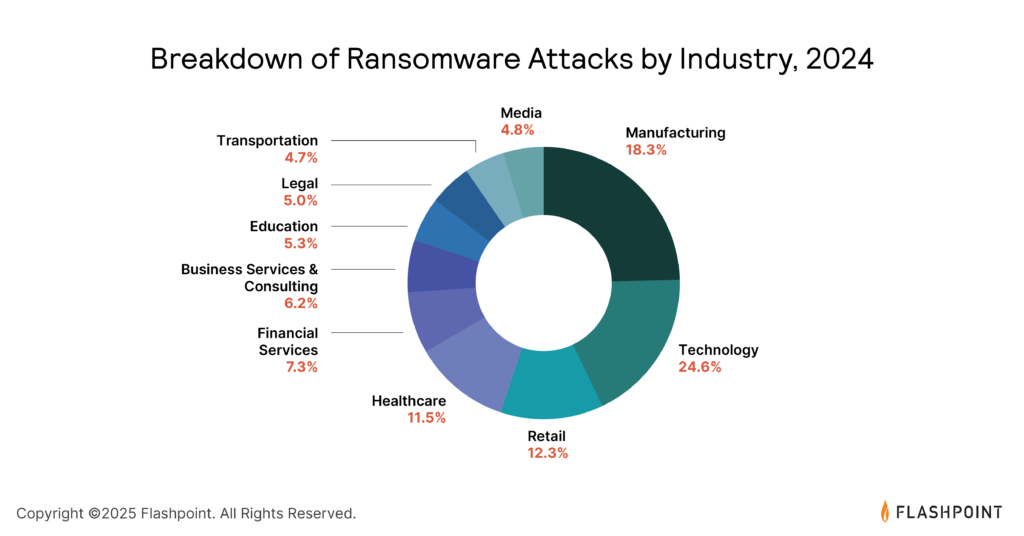
why? Almost every organization operating in this sector is rich in highly sensitive information, including patient data, treatment documents, and financial records related to patient insurance. Furthermore, affected healthcare organizations are more likely to pay ransom, as network disruptions can cease completely, leading to patient death.
Proliferation as a ransomware service
Ransomware remains a tragedy, with Flashpoint analysts already collecting more than 1,462 ransomware attacks in 2025. It first emerged in 1989 and rapidly evolved from opportunistic attacks launched by lonely threat actors to a vast, institutional enterprise driven by the proliferation of readily available tools and services.
Today's ransomware landscape is dominated by the business model (RAAS) activities adopted by cybercriminals. Users purchase illegal licenses that allow them to access complex code, updates, customer support, keyloggers, miners, botnets and other tools.
Raas, which acts as a multiplier of force, significantly lowered the entry barrier, allowing even unsleashed attackers to leverage these complex tools against victims. Especially the healthcare sector.
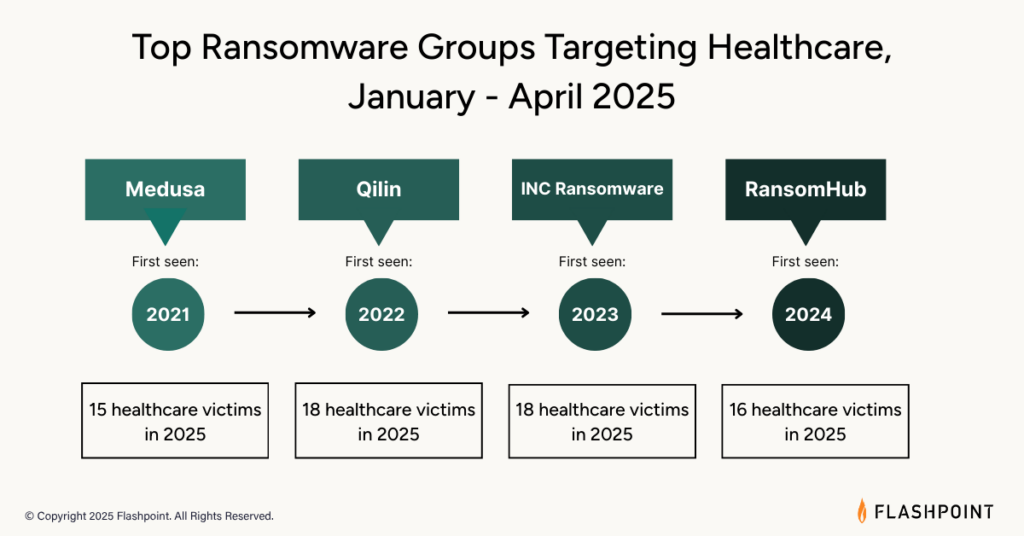
From January to April 2025, FlashPoint observed a total of 181 medical victims. The next RAAS group is the most prolific.
giraffe
Qilin first appeared in July 2022. Originally operated under the name “Agenda”, Qilin became one of the most prolific ransomware groups in 2024. However, Qilin is known to target other industries, such as manufacturing, financial services and education. Between January and April 2025, Qilin ransomed 18 publicly disclosed victims in the health care sector.
Qilin ransomware, which is likely to have borne Russia, usually infects victims using spear phishing campaigns, remote monitoring and management (RMM) tools, and cobalt strike malware. Ransomware can be used to avoid detection using vulnerable SYS drivers and propagated through Psexec and SecureShell.
Like many other ransomware groups, Qilin is well known for its dual-terr technology, which involves requesting random payments to prevent data leaks in illegal forums and markets.
INC ransomware
INC has been operating since July 2023. Like Qilin, the group targets 18 publicly disclosed healthcare sector victims and uses double fear technology. The INC targets primarily the healthcare industry, but attack organizations in other fields, including education, technology and government, have been observed.
Initial infections usually date back to spearfishing lures, but Inc has recently utilized an exploit affecting CVE-2023-3519. This exploit can create stack-based buffer overflows and allow for the execution of arbitrary code.
A recent Verizon study shows ransomware is currently disproportionately affecting small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs). This is a trend seen in Inc's targeting as well. At the moment, many of the INC victims are small businesses with up to 1,000 employees, with the group focusing on targets of hospitals and health service providers.
Ransom Hub
A relatively new group, Ransomhub, first appeared in February 2024. Between January and April 2025, the group was responsible for targeting 16 publicly-published victims in the healthcare sector. Ransomhub also gained notoriety for its involvement in high-profile ransomware attacks.
Flashpoint analysts observe that Ransomhub gains initial access by leveraging CVE-2020-1472. This is a vulnerability that allows domain privileges to escalate and start control. No user interaction is required to take advantage of this exploit. It makes the ideal tool to throw away the requirements of social engineering.
Ransomhub's “Locker” ransomware is written in Golang and C++ and is supported by Windows, Linux, and ESXi. During the attack, FlashPoint observed the group that it used the incorrect cloud storage instance to target system backups.
Medusa
First introduced in June 2021, Medusa has become one of the top active ransomware groups targeting the healthcare sector, targeting 15 casualties between January and April 2025.
Medusa is best known for its rapid encryption and unique technology for spreading malware. The group made infamous in 2023 for attacking public schools. They demand a ransom of $1 million (USD).
To infect victims, Medusa relies on two early access vectors: phishing and vulnerability exploits. Medusa is known to take advantage of the Screenconnect vulnerability (CVE-2024-1709). This causes a remote attacker to start the setup wizard to create an administrative user and create a Fortinet EMS SQL Indection vulnerability (CVE-2023-48788) that allows SQL Quelie injection or manipulation.
Protect against ransomware using flashpoints
The relentless evolution and proliferation of ransomware, particularly through the RAAS model, continues to pose a major threat to the healthcare sector. Security teams need to be vigilant and proactive in their defense strategies as threat actors improve their tactics and leverage phishing and vulnerability exposure.
Understanding the specific techniques and advantageous access points of outstanding ransomware groups is an important first step in preventing and mitigating the potentially catastrophic effects of these attacks. Download the 2025 Ransomware Survival Guide and learn how Flashpoints provide a holistic approach to ransomware defense.

